A) The price level measured by the implicit price deflator is on the horizontal axis and real GDP is on the vertical axis.
B) The price level measured by the consumer price index is on the vertical axis and real GDP is on the horizontal axis.
C) The price level measured by the implicit price deflator is on the vertical axis and real GDP is on the horizontal axis.
D) The price level measured by the implicit price deflator is on the vertical axis and employment is on the horizontal axis.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the international trade effect, holding everything else unchanged,
A) an increase in net exports shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
B) an increase in the domestic price level reduces net exports leading to a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
C) an increase in the exchange rate shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
D) an increase in the price level of foreign goods reduces imports leading to a movement along the domestic economy's aggregate demand curve.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that product prices start rising but nominal wages do not. In that case,
A) real wages will fall and firms will want to produce more because doing so will be profitable.
B) real wages will rise and firms will want to produce more because doing so will be profitable.
C) there will be a surplus of goods and services produced.
D) there will be a shortage of goods and services produced.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true of the economy in the long run? In the long run, I. real GDP eventually moves to potential output because all wages and prices are assumed to be flexible. II. the economy can achieve its natural level of employment and potential output at any price level. III. there is no cyclical unemployment.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short run in macroeconomic analysis is a period
A) in which wages and some other prices do not respond to changes in economic conditions.
B) in which full wage and price flexibility and market adjustment have been achieved.
C) of less than 12 months.
D) in which all macroeconomic variables are fixed.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, predict what happens in the short run if an increase in health insurance premiums paid by firms raises the cost of employing each worker.
A) The aggregate supply curve shifts right; the aggregate demand curve is not affected; price level decreases; real GDP increases.
B) The aggregate demand curve shifts right; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real GDP increase.
C) The aggregate demand curve shifts left; the aggregate supply curve is not affected; price level and real GDP decrease.
D) The aggregate supply curve shifts left; the aggregate demand curve is not affected; price level increases; real GDP decreases.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The use central bank policies to influence the level of economic activity is called
A) banking and finance policy.
B) financial market policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) congressional policy.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A change in the price level, all other things unchanged, causes
A) a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
B) a shift of the aggregate demand curve.
C) both a movement along the aggregate demand curve and a shift in the curve.
D) no change in the value of assets held in the form of money.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-1 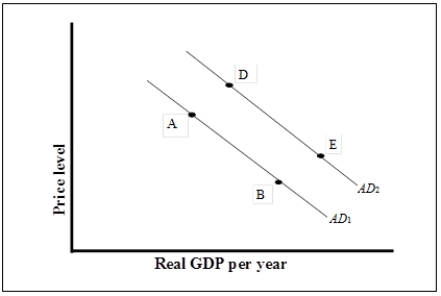 -Refer to Figure 7-1. What could have caused a movement from point D to point A?
-Refer to Figure 7-1. What could have caused a movement from point D to point A?
A) An increase in the economy's general price level
B) A decrease in investment demand due to lower expected sales
C) A decrease in capital gains taxes
D) An increase in money supply that lowers interest rate
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-6 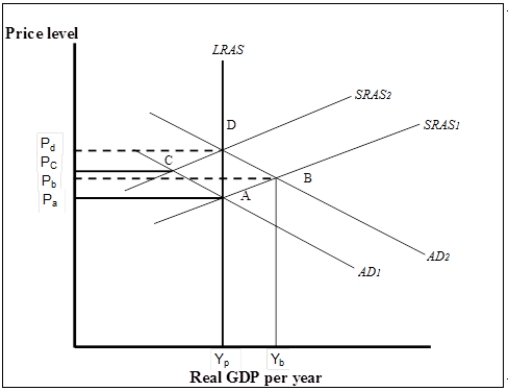 -Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. A shift from AD1 to AD2 could have been caused by all of the following except
-Refer to Figure 7-6. Suppose the economy is initially in short-run equilibrium at B. A shift from AD1 to AD2 could have been caused by all of the following except
A) an increase in consumer optimism.
B) economic prosperity in foreign economies.
C) a personal income tax cut.
D) an increase in the price level from Pa to Pb.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How will a recession in the economies of our foreign trading partners affect U.S. aggregate demand?
A) It will have no effect on our aggregate demand.
B) U.S. aggregate demand will increase.
C) U.S. aggregate demand will decrease.
D) It depends on whether the U.S. offers financial aid to these countries.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-1  -Refer to Figure 7-1. What could have caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right from AD1 to AD2?
-Refer to Figure 7-1. What could have caused the aggregate demand curve to shift to the right from AD1 to AD2?
A) An increase in exports
B) An increase in imports
C) A decrease in defense spending
D) An increase in the domestic price level
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-3 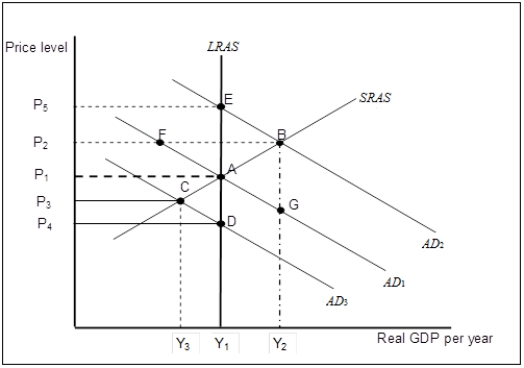 -Refer to Figure 7-3. Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose the stock market crashes, significantly reducing household wealth. What happens in the long-run, all other things unchanged?
-Refer to Figure 7-3. Suppose that the economy is in long-run equilibrium at point A. Now suppose the stock market crashes, significantly reducing household wealth. What happens in the long-run, all other things unchanged?
A) The aggregate demand curve will shift back to AD1.
B) The economy will be stuck at an output level below its potential level.
C) The economy returns to full-employment equilibrium at point A.
D) The economy returns to full-employment equilibrium at point D.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the interest rate effect that explains why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward?
A) It refers to the effect of changes in the price level on quantity of investment demanded which in turn affects interest rates.
B) It refers to the effect of interest rates on borrowing which in turn affects consumption spending.
C) It refers to the effect of changes in the price level on interest rates which in turn affects the quantity of investment demanded.
D) It refers to the shifts in aggregate demand when interest rates change.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose net exports decreases by $100 million due to a slump in foreign economies. If the the value of the multiplier is 2, what happens to the domestic aggregate demand curve?
A) Since less will be produced, the aggregate demand does not shift. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the left by $100 million at each price level.
B) It shifts to the left by $50 million at each price level.
C) It shifts to the left by $100 million at each price level.
D) It shifts to the left by $200 million at each price level.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the long run, real output can be less than, equal to, or greater than the economy's potential output.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-2 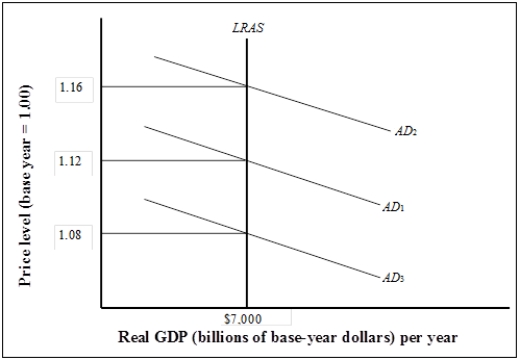 -Refer to Figure 7-2. If the real GDP is $7,000 billion and the implicit price deflator is 1.16, what is the value of nominal GDP?
-Refer to Figure 7-2. If the real GDP is $7,000 billion and the implicit price deflator is 1.16, what is the value of nominal GDP?
A) $6,034 billion
B) $8,120 billion
C) $9,120 billion
D) cannot be determined from the information given
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aggregate demand is defined as
A) the demand for goods and services generated by all sectors in the economy, holding price level constant.
B) the relationship between the total quantity of goods and services demanded and the price level, all other determinants of spending unchanged.
C) the relationship between the total quantity of goods and services demanded and the supply of factors of production, all other determinants of production unchanged.
D) the relationship between the total quantity of goods and services demanded and the income level, all other determinants of spending unchanged.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 7-7 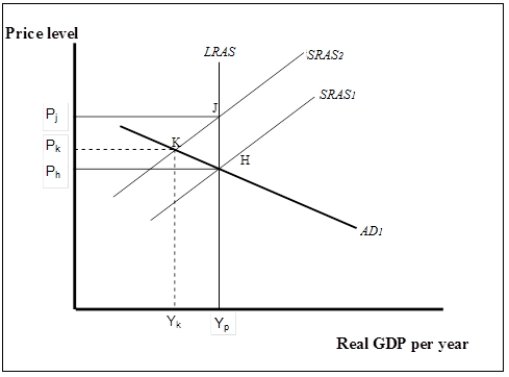 -Refer to Figure 7-7. Suppose the economy is initially at K. Which of the following statements best explains how the economy responds to restore long-run macroeconomic equilibrium?
-Refer to Figure 7-7. Suppose the economy is initially at K. Which of the following statements best explains how the economy responds to restore long-run macroeconomic equilibrium?
A) Over time, the aggregate demand curve will shift to the right until long-run equilibrium is restored at J and the gap is closed.
B) Rising unemployment puts pressure on nominal wages to fall. The SRAS curve shifts right to SRAS1 closing the gap at H.
C) In response to rising prices, firms will increase production moving along SRAS2 until long- run equilibrium is restored at J and the gap is closed.
D) Rising unemployment puts pressure on nominal wages to fall. Firms employ more workers moving along SRAS2 until long-run equilibrium is restored at J and the gap is closed.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, a decrease in aggregate demand, all other things unchanged, will cause the price level to
A) increase and potential output to increase.
B) decrease and potential output to decrease.
C) increase and potential output to remain stable.
D) decrease and potential output to remain stable.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 166
Related Exams