A) manipulating the independent variable caused the changes in the dependent variable.
B) the independent and dependent variables were correlated but not necessarily causally related.
C) the variables were defined optimally in terms of validity.
D) the same results would be obtained if we replicated the experiment in a different population.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A set of rules and techniques for observation is termed an empirical:
A) theory.
B) study.
C) definition.
D) method.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
People are more critical of new evidence that is:
A) consistent with common sense.
B) consistent with their attitudes or beliefs.
C) inconsistent with their attitudes or beliefs.
D) presented using emotionally charged language.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An academic clinical psychologist uses Beck's Depression Inventory,a validated scale with scores ranging from 0 to 63,with higher scores indicating greater levels of depression,to measure depression levels in the population of 1,000 incoming freshmen students.She creates a frequency distribution of her findings.What should be displayed on the vertical axis?
A) the number of times each possible score occurred
B) each possible score
C) the mean of the 1,000 scores
D) the categorical labels "Not Depressed" and "Depressed"
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a classic experiment,psychology students were assigned to work either with "bright" rats or with "dull" rats,described as such by the experimenter.In a task involving learning a maze,rats arbitrarily labelled as "bright" learned the maze faster than did rats arbitrarily labelled as "dull." The experimenter suspected that the psychology students with "bright" rats took the learning task more seriously,and this was reflected in their rats' performance.This finding illustrates how:
A) expectations can influence observations.
B) observations can influence measurement.
C) expectations can influence reality.
D) observations can influence reality.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A sample taken from a population is signified by a lowercase n.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which characteristic describes a normal distribution?
A) It is symmetrical around a single peak in the middle.
B) It has a peak at each end of the distribution.
C) It is skewed to one side or the other.
D) It resembles a straight line.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an experiment,researchers exposed half of the participants to loud noise during a memory-encoding task.The room was quiet for the other half of the participants.Later,all participants were given a memory test and the number of correct items recalled was obtained for each participant.The participants who encoded information in the noisy room constitute the:
A) independent variable.
B) dependent variable.
C) experimental group.
D) control group.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
David engages in unethical research practices and changes the result of a statistical test from an otherwise ethically conducted study.David is engaged in:
A) data fabrication.
B) data falsification involving fudging the results.
C) suppressing data inconsistent with the study's goals.
D) willfully ignoring principles of beneficence and justness.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A frequency distribution in which most measurements are concentrated around the mean and fall off towards the tails,and where the two sides of the distribution are symmetrical,is called a _____ distribution.
A) normal
B) positively skewed
C) negatively skewed
D) standard
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Describing length as "change in the location of light over time" is an example of a(n) :
A) measurement device.
B) casual observation.
C) unit of measurement.
D) operational definition.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A correlation coefficient (r)can range from 0 to 100.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Five extremely tall members of the university basketball team are among 30 students in an introductory psychology class.If a frequency distribution is taken of height,the distribution probably will be:
A) normal.
B) positively skewed.
C) negatively skewed.
D) bimodal.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phrase "n = 1" means that:
A) the results are not statistically significant.
B) there is a perfect correlation between two variables.
C) there is only one participant in the study.
D) there is only one independent variable.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement describes a difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
A) A hypothesis establishes a general principle through experiments,whereas a theory is based on a specific observation that is limited to a single instance.
B) A hypothesis explains a set of theories,whereas a theory explains a set of laws.
C) A hypothesis is a falsifiable prediction made by a theory,whereas a theory is a hypothetical explanation of a natural phenomenon.
D) A hypothesis needs to be proven to be true,whereas a theory is inherently true.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reliable measure is one that:
A) tends to produce the same result whenever it is used to measure the same thing.
B) tends to differentiate between accurate and inaccurate data.
C) compensates for a weak operational definition of a property under study.
D) is necessarily an accurate measure of an underlying property.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions 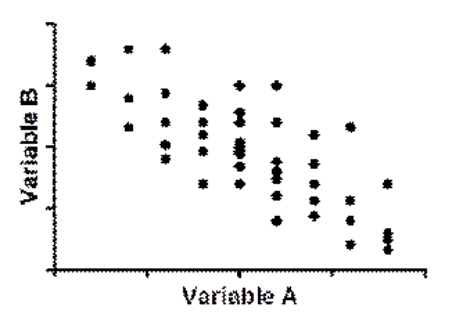 -(Scenario I) Which statement is true given that variables A and B are significantly correlated?
-(Scenario I) Which statement is true given that variables A and B are significantly correlated?
A) Variable A causes variable B OR variable B causes variable A.
B) Knowing the score on variable A allows for an estimate of the score on variable B.
C) There is no causal relationship between the two variables.
D) A third variable cannot be responsible for the observed association.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A _____ correlation is associated with a less-is-more relationship.
A) negative
B) positive
C) strong
D) weak
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A frequency distribution graphically displays the:
A) number of times each measurement occurs.
B) probability of obtaining a particular measurement.
C) rate at which a target behaviour occurs.
D) average derived from a set of measurements.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an experiment,researchers exposed half of the participants to loud noise during a memory-encoding task.The room was quiet for the other half of the participants.Later,all participants were given a memory test and the number of correct items recalled was obtained for each participant.What is the independent variable?
A) the number of items recalled
B) the noise level during the encoding task
C) the time interval between encoding and recall
D) the probability of being assigned to the two groups
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 400
Related Exams