A) rewarding increases in human capital.
B) paying efficiency wages.
C) practicing discrimination.
D) paying a compensating differential.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One example of labor-market discrimination is that firms may be less likely to interview job-market candidates whose names suggest that they are members of a racial minority.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct?
A) Some economists believe that business owners who emphasize profit maximization will hire the most productive workers regardless of the personal characteristics of the worker; hence, these firms will drive discriminating firms out of business.
B) Two economists found that employers in Boston and Chicago were about 50 percent more likely to interview job applicants named Emily and Greg than those named Lakisha and Jamal.
C) Two economists found that women were less likely to participate in an experiment where they were paid based on math skills but more likely to participate when they were paid based on reading skills; men were more likely to participate when they were paid based on math skills and less likely to participate when they were paid based on reading skills.
D) Economists found that the prices of older baseball cards were about 10 percent lower when the player was black rather than white.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements accurately explains the superstar phenomenon in wages?
A) Better carpenters earn more than average carpenters because people are willing to pay higher prices for higher-quality work.
B) The more productive an author is, the more books she can write each year, so the more she earns.
C) Talented movie stars earn more than equally talented mechanics because technology allows the delivery of the services provided by the movie stars to all interested customers.
D) Athletes get paid for performing services that everyday people perform as hobbies.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Studies have shown that union workers earn about
A) 10 to 20 percent more than nonunion workers in similar jobs.
B) 10 to 20 percent less than nonunion workers in similar jobs.
C) 40 to 50 percent more than nonunion workers in similar jobs.
D) 40 to 50 percent less than nonunion workers in similar jobs.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increases in international trade and technological change have been offered as explanations for the
A) increase in demand for both skilled and unskilled workers in the United States.
B) increase in demand for skilled workers and decrease in demand for unskilled workers in the United States.
C) decrease in demand for skilled workers and increase in demand for skilled workers in the United States.
D) decrease in demand for both skilled and unskilled workers.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an employer pays a man a higher wage than a woman, the employer
A) is discriminating against the woman but is still maximizing profit.
B) is not discriminating against the woman.
C) may or may not be discriminating against the woman.
D) is discriminating against the woman and is not maximizing profit.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Evidence suggests that business owners are generally
A) interested in profits only when discrimination is illegal.
B) more interested in discrimination than in making a profit.
C) unable to determine the link between discrimination and profitability.
D) more interested in making a profit than in discriminating against a particular group.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a "superstar" to emerge, it must be the case that
A) it is possible to supply the good or service that the superstar produces at low cost to every customer.
B) some customers are willing and able to pay large sums of money to enjoy the good or service provided by the superstar.
C) the superstar has a natural monopoly on his or her good or service.
D) the superstar can become sufficiently popular to earn income from advertisements.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the supply of workers is plentiful, one would predict that market wages would be
A) determined outside the domain of economic theory.
B) determined solely by factors that affect demand.
C) low, other things equal.
D) high, other things equal.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It is likely that, if we could measure the quality as well as the quantity of education,
A) the human-capital argument would become less compelling as a means of explaining wage differentials between white workers and black workers.
B) the human-capital argument would become less compelling as a means of explaining wage differentials between male workers and female workers.
C) wage differentials between white workers and black workers would be more puzzling than they are now.
D) wage differentials between white workers and black workers would be more fully explained.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The differences in the desirability of different jobs within a company could give rise to a compensating differential between workers.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Figure 19-7 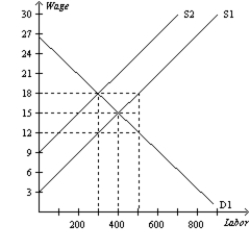 -Refer to Figure 19-7. The figure shows labor demand and labor supply in a non-unionized labor market. If the current labor demand is D1 and the current labor supply is S1, when a minimum wage of $18 per hour is imposed in this market, how many unemployed workers result?
-Refer to Figure 19-7. The figure shows labor demand and labor supply in a non-unionized labor market. If the current labor demand is D1 and the current labor supply is S1, when a minimum wage of $18 per hour is imposed in this market, how many unemployed workers result?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Offering different opportunities to similar individuals who differ only by race, ethnic group, sex, age, or other personal characteristics is called
A) a compensating differential.
B) an efficiency wage.
C) discrimination.
D) compensating variation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over the past several years, the earnings gap between high-skilled and low-skilled workers has widened because (i) international trade has altered the relative demand for skilled and unskilled labor. (ii) changes in technology have altered the relative demand for skilled and unskilled labor. (iii) the return to education for men has decreased, whereas the return to education for women has increased.
A) (i) only
B) (iii) only
C) (i) and (ii) only
D) (i) , (ii) , and (iii)
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what way do competitive markets have a "natural remedy" for discriminatory hiring practices?
A) Governments regulate to resolve problems of discrimination.
B) Profit-maximizing firms that do not discriminate tend to replace firms that discriminate.
C) Wages paid to groups that are victimized by discrimination are eventually bid up to above-equilibrium levels.
D) Discrimination is usually the outcome of rational decision-making processes, and competitive markets produce rational outcomes.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the signaling view, education
A) has no effect on lifetime earnings.
B) alters work ethic.
C) enhances productivity.
D) is an indicator of natural ability.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The superstar phenomenon explains why professional athletes earn more than amateur athletes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following explains why soccer players make millions of dollars in Europe but do not in the United States?
A) discriminatory rules established by the government
B) compensating wage differentials for living in Europe
C) discriminatory preferences on the part of US sports fans for other sports
D) efficiency wages paid to European players to enhance on-field performance
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Construction work is much riskier than working as a server at a restaurant. As a result, we'd expect a difference in wages between the two jobs. The difference is known as
A) an efficiency wage.
B) a compensating differential.
C) a wage adjustment.
D) a minimum wage.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 511
Related Exams