A) tax avoidance
B) tax evasion
C) a tax return compensation plan
D) activities outside the intent of tax law
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is one of the most difficult issues associated with trying to structure a tax policy to satisfy horizontal equity
A) determining whether or not a taxpayer falls within the highest income quintile
B) determining the level of transfer payments made to low-income groups
C) determining the source of income for taxpayers
D) determining what differences are relevant to a family's ability to pay
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What are taxes on specific goods such as cigarettes,gasoline,and alcoholic beverages called
A) sales taxes
B) excise taxes
C) social insurance taxes
D) consumption taxes
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From which source do provincial and local governments NOT generate revenue
A) sales taxes
B) the federal government
C) corporate income taxes
D) customs duties
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Vertical equity is not consistent with a regressive tax structure.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
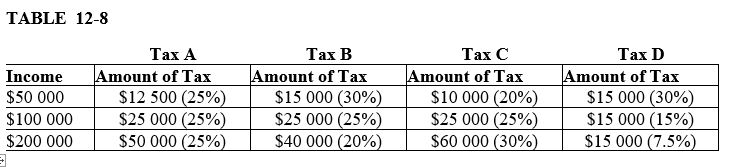 -Refer to Table 12-8.Which tax illustrates a regressive tax
-Refer to Table 12-8.Which tax illustrates a regressive tax
A) tax A
B) tax B
C) tax C
D) tax D
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The federal government collects taxes in a number of ways.Which of the following ranks the following sources of revenue from the largest to the smallest
A) corporate income taxes, GST, personal income taxes, and excise taxes and duties
B) corporate income taxes, EI payroll taxes, personal income taxes, and excise taxes and duties
C) personal income taxes, corporate income taxes, excise taxes and duties, and GST
D) personal income taxes, corporate income taxes, GST, and excise taxes and duties
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The federal government collects about one-half of the taxes in our economy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is total taxes paid divided by total income
A) the lump-sum tax liability
B) the marginal tax rate
C) the average tax rate
D) the average consumption tax liability
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the government taxes labour earnings,what can we expect people to do
A) work more so they can keep the same standard of living
B) work less and enjoy more leisure
C) quit their present job and find one that pays better
D) stop working altogether and go on welfare in protest
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens when interest income from savings is taxed
A) For the poor people, more will be saved than without the tax to make up for what is lost in taxes.
B) For the rich people, more will be saved than without the tax to make up for what is lost in taxes.
C) For the rich people, less will be saved than without the tax since tax lowers the return on income.
D) For the poor people, less will be saved without tax since tax lowers the cost of investment.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Scenario 12-1 Suppose Jeremy and Kelsey receive great satisfaction from their consumption of turkey.Kelsey would be willing to purchase only one slice and would pay up to $5 for it.Jeremy would be willing to pay $8 for his first slice, $6 for his second slice, and $2 for his third slice.The current market price is $2 per slice. -Refer to Scenario 12-1.If a tax of $4 is levied on each slice of turkey,what is the deadweight loss of the tax
A) $3
B) $6
C) $8
D) $9
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While debate over tax policy is complex,how do economists play an important role
A) by arguing for policies that clearly lead to efficiency gains in the economy
B) by shedding light on the tradeoff between efficiency and equity in tax policy
C) by articulating the importance of equity as the most important goal of tax policy
D) by demonstrating that there are no tradeoffs in tax policy: both efficiency and equity can be attained if the tax policy follows basic economic reasoning
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the ranking of the following provincial and local government expenditure categories from largest to smallest
A) health, education, social services
B) debt service, health, education
C) social services, debt service, education
D) health, social services, education
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does the average tax rate measure
A) the fraction of spending paid in taxes
B) the fraction of income paid in taxes
C) the incremental rate of tax on income
D) the average deadweight loss from all taxes
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement best describes tax evasion
A) It is facilitated by legal deductions to taxable income.
B) It is the same as tax avoidance.
C) It is recommended by the Canadian Accounting Association.
D) It is illegal.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does horizontal equity state that taxpayers with similar incomes should pay
A) taxes based only on their income
B) exactly the same amount of taxes, regardless of circumstances
C) similar amounts of tax
D) taxes based on the benefits received from government services
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is an income tax in which the average tax rate is the same for all taxpayers
A) a progressive tax
B) a regressive tax
C) a distortion-free tax
D) a proportional tax
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
MaKenna earns income of $80,000 per year.Her average tax rate is 50 percent.MaKenna paid $7000 in taxes on the first $30,000 she earned.What was the marginal tax rate on the first $30,000 she earned,and what was the marginal tax rate on the remaining $50,000
A) 16.25 percent and 50.00 percent
B) 18.00 percent and 60.00 percent
C) 20.00 percent and 20.00 percent
D) 23.33 percent and 66 percent
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does tax incidence refer to
A) what product or service the tax is levied on
B) who bears the tax burden
C) what sector of the economy the imposed tax most affects
D) the impact a tax will have on the economy
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 200
Related Exams