A) the marginal benefit from another bicycle is greater than the marginal cost of another bicycle.
B) more bicycles must be produced to reach the efficient level of output.
C) fewer bicycles must be produced to reach the efficient level of output.
D) the economy is efficient at this level of production of bicycles.
E) both A and B.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 2.1.1
The following table gives points on the production possibilities frontier for goods X and Y.
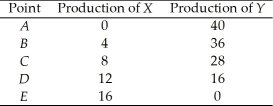 -From the data in Table 2.1.1, the production of 7 units of X and 28 units of Y is
-From the data in Table 2.1.1, the production of 7 units of X and 28 units of Y is
A) unattainable.
B) attainable but leaves some resources unused or misallocated or both.
C) on the PPF between points C and D.
D) on the PPF between points B and C.
E) outside the PPF.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The production possibilities frontier shows
A) the maximum possible rate of growth of output in an economy.
B) the maximum quantity of resources available at any given time.
C) the maximum level of production that can be attained.
D) combinations of goods and services that do not fully use available resources.
E) the effect of advancing technology on production possibilities.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fact that resources are not equally productive in all activities
A) implies that a production possibilities frontier will be bowed outward.
B) implies that gains from specialization and trade are unlikely.
C) follows from the law of demand.
D) implies a linear production possibilities frontier.
E) implies that an economy should not produce certain goods.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
Table 2.4.1
The planets of Vulcan and Romulus each produce goods X and Y.
The following table gives points on their production possibilities frontiers.
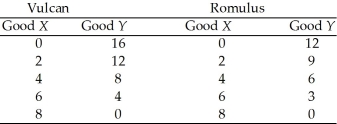 -Refer to Table 2.4.1.For Romulus, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of Y is
-Refer to Table 2.4.1.For Romulus, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of Y is
A) 2/3 units of X.
B) 1/2 unit of X.
C) 2 units of X.
D) 3 units of X.
E) 3/2 units of Y.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a hurricane causes extensive devastation, destroying houses, roads, schools and factories.What would be the effect of this hurricane on a production possibilities frontier consisting of consumption goods and capital goods?
A) It would shift outward at all points.
B) It would shift inward at all points.
C) There would be a movement along the existing production possibilities frontier towards a less capital-intensive point.
D) There would be a movement along the existing production possibilities frontier towards a more capital-intensive point.
E) There would be a movement from the existing production possibilities frontier inwards towards a point with unused or misallocated resources.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the production possibilities frontier for skirts and pants is a straight line.As the production of skirts increases, the marginal benefit from skirts
A) increases and marginal cost is constant.
B) is constant and marginal cost decreases.
C) decreases and marginal cost increases.
D) decreases and marginal cost decreases.
E) decreases and marginal cost is constant.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
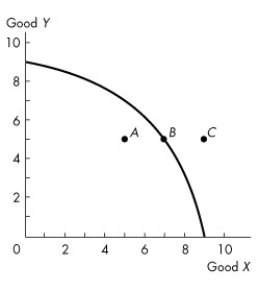 Figure 2.1.1
-Complete the following sentence.In Figure 2.1.1,
Figure 2.1.1
-Complete the following sentence.In Figure 2.1.1,
A) movement from A to B would require a technological advance.
B) point B is a point of production efficiency.
C) some resources must be unused at point C.
D) the concept of decreasing opportunity cost is illustrated.
E) movement from C to B would require a technological improvement.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
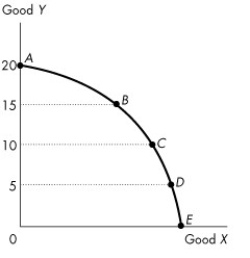 Figure 2.1.3
-Refer to the production possibilities frontier in Figure 2.1.3.The fact that less of X must be given up when moving from D to C than when moving from B to A indicates
Figure 2.1.3
-Refer to the production possibilities frontier in Figure 2.1.3.The fact that less of X must be given up when moving from D to C than when moving from B to A indicates
A) decreasing opportunity cost.
B) increasing opportunity cost.
C) comparative advantage in the production of X.
D) the consequences of technological improvement.
E) unemployed resources at D.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A production possibilities frontier is negatively sloped because
A) more goods are purchased as price falls.
B) of opportunity cost.
C) some resources are unused.
D) there is not enough capital in the economy.
E) of increasing consumption.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 2.1.1
The following table gives points on the production possibilities frontier for goods X and Y.
 -Refer to Table 2.1.1.The opportunity cost of increasing the production of X from 8 to 12 units is
-Refer to Table 2.1.1.The opportunity cost of increasing the production of X from 8 to 12 units is
A) 4 units of X.
B) 4 units of Y.
C) 8 units of Y.
D) 12 units of Y.
E) 16 units of Y.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a production possibilities frontier with corn production measured on the vertical axis and car production measured on the horizontal axis.Unusually good weather for growing corn shifts
A) the horizontal intercept of the PPF rightward and the vertical intercept of the PPF upward.
B) the horizontal intercept of the PPF rightward but does not shift the vertical intercept of the PPF.
C) the vertical intercept of the PPF upward but does not shift the horizontal intercept of the PPF.
D) neither the horizontal intercept nor the vertical intercept of the PPF.
E) the vertical intercept of the PPF downward and the horizontal intercept of the PPF leftward.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a PPF that measures the production of quilts on the y-axis and the production of pillows on the x-axis.As the firm moves along this PPF, the quantities of
A) all goods other than pillows and quilts are decreasing.
B) all goods other than pillows and quilts remain constant.
C) all goods other than pillows and quilts are increasing.
D) pillows and quilts produced increase together.
E) pillows and quilts produced decrease together.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
Table 2.4.1
The planets of Vulcan and Romulus each produce goods X and Y.
The following table gives points on their production possibilities frontiers.
 -Refer to Table 2.4.1.For Romulus, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of X is
-Refer to Table 2.4.1.For Romulus, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of X is
A) 4 units of Y.
B) 2 units of Y.
C) 2/3 units of Y.
D) 1 unit of Y.
E) 3/2 units of Y.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
Table 2.4.1
The planets of Vulcan and Romulus each produce goods X and Y.
The following table gives points on their production possibilities frontiers.
 -Refer to Table 2.4.1.For Vulcan, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of X is
-Refer to Table 2.4.1.For Vulcan, the opportunity cost of producing an additional unit of X is
A) 4 units of Y.
B) 2 units of Y.
C) 2/3 units of Y.
D) 1 unit of Y.
E) dependent upon how many units of X are already produced.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The production possibilities frontier
A) is the boundary between attainable and unattainable levels of production.
B) is the boundary between what we want to consume and what we want to produce.
C) shows how production increases as prices rise.
D) shows prices at which production is possible and impossible.
E) illustrates why there need not be any scarcity in the world.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A movement along the production possibilities frontier will result from
A) technological change.
B) a change in the stock of capital.
C) a change in the labour force.
D) a change in human capital
E) none of the above.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following quotations illustrates economic growth?
A) "The firm should lower the price it charges for widgets and gadgets."
B) "The firm should sell more gadgets, even if it means less widget sales."
C) "The more and more gadgets the firm produces, the bigger the fall in widget production."
D) "If the firm invests more in capital equipment, it can expand production next year."
E) "The firm has been able to lower costs due to its extensive experience in building widgets."
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main functions of markets include
A) promoting the social interest, but not the self-interest.
B) selling goods, but not factors of production.
C) enabling buyers and sellers to get information about each other.
D) establishing a physical location for business transactions.
E) promoting the self-interest, but not the social interest.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The concept of opportunity cost
A) cannot be explained by using a production possibilities frontier.
B) explains that goods are swapped for other goods.
C) implies that when a person is more efficient in the production of one good, he should produce that good and exchange it for some good that he is relatively less efficient at producing.
D) implies that a double coincidence of wants must be present for exchange to take place.
E) implies that because productive resources are scarce, we must give up some of one good to acquire more of another.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 159
Related Exams