B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Although goodwill created in a merger may not be amortized for shareholder reporting purposes,it may be amortized for Federal tax purposes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A congeneric merger is one where the merging firms operate in related businesses but do not necessarily produce the same products or have a producer-supplier relationship.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Merger activity is likely to heat up when interest rates are high because target firms can expect to receive an especially high premium over the pre-announcement stock price.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The present value of the free cash flows discounted at the unlevered cost of equity is the value of the firm's operations if it had no debt.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Synergistic benefits can arise from a number of different sources,including operating economies of scale,financial economies,and increased managerial efficiency.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Juicers Inc.is thinking of acquiring Fast Fruit Company.Juicers expects Fast Fruit's NOPAT to be $9 million the first year,with no net new investment in operating capital and no interest expense.For the second year,Fast Fruit is expected to have NOPAT of $25 million and interest expense of $5 million.Also,in the second year only,Fast Fruit will need $10 million of net new investment in operating capital.Fast Fruit's marginal tax rate is 40%.After the second year,the free cash flows and the tax shields from Fast Fruit to Juicers will both grow at a constant rate of 4%.Juicers has determined that Fast Fruit's cost of equity is 17.5%,and Fast Fruit currently has no debt outstanding.Assume that all cash flows occur at the end of the year,Juicers must pay $45 million to acquire Fast Fruit.What it the NPV of the proposed acquisition? Note that you must first calculate the value to Juicers of Fast Fruit's equity.
A) $45.0 million
B) $68.2 million
C) $86.5 million
D) $113.2 million
E) $133.0 million
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are legal and acceptable reasons for the high level of merger activity in the U.S.during the 1980s?
A) A profitable firm acquires a firm with large accumulated tax losses that may be carried forward.
B) Attempts to stabilize earnings by diversifying.
C) Purchase of assets below their replacement costs.
D) Reduction in competition resulting from mergers.
E) Synergistic benefits arising from mergers.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 26.1 Best Window & Door Corporation is considering the acquisition of Glassmakers Inc. Glassmakers has a capital structure consisting of $5 million (market value) of 11% bonds and $10 million (market value) of common stock. Glassmakers' pre-merger beta is 1.36. Best's beta is 1.02, and both it and Glassmakers face a 40% tax rate. Best's capital structure is 40% debt and 60% equity. The free cash flows from Glassmakers are estimated to be $3.0 million for each of the next 4 years and a horizon value of $10.0 million in Year 4. Tax savings are estimated to be $1 million for each of the next 4 years and a horizon value of $5 million in Year 4. New debt would be issued to finance the acquisition and retire the old debt, and this new debt would have an interest rate of 8%. Currently, the risk-free rate is 6.0% and the market risk premium is 4.0%. -Refer to Exhibit 26.1.What is Glassmakers' pre-merger WACC?
A) 9.02%
B) 9.50%
C) 9.83%
D) 10.01%
E) 11.29%
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most defensive mergers occur as a result of managers' actions to maximize shareholders' wealth.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A spin-off is a type of divestiture in which the assets of a division are sold to another firm.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a petrochemical firm that used oil as feedstock merged with an oil producer that had large oil reserves and a drilling subsidiary,this would be a vertical merger.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Since a manager's central goal is to maximize the firm's stock price,any merger offer that provides stockholders with significant gains over the current stock price will be approved by the current management team.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is most CORRECT?
A) The smaller the synergistic benefits of a particular merger, the greater the scope for striking a bargain in negotiations, and the higher the probability that the merger will be completed.
B) Since mergers are frequently financed by debt rather than equity, a lower cost of debt or a greater debt capacity are rarely relevant considerations when considering a merger.
C) Managers who purchase other firms often assert that the new combined firm will enjoy benefits from diversification, including more stable earnings. However, since shareholders are free to diversify their own holdings, and at what's probably a lower cost, diversification benefits is generally not a valid motive for a publicly held firm.
D) Operating economies are never a motive for mergers.
E) Tax considerations often play a part in mergers. If one firm has excess cash, purchasing another firm exposes the purchasing firm to additional taxes. Thus, firms with excess cash rarely undertake mergers.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A conglomerate merger occurs when two firms with either a horizontal or a vertical business relationship combine.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about valuing a firm using the APV approach is most CORRECT?
A) The horizon value is calculated by discounting the free cash flows beyond the horizon date and any tax savings at the cost of debt.
B) The horizon value is calculated by discounting the expected earnings at the WACC.
C) The horizon value is calculated by discounting the free cash flows beyond the horizon date and any tax savings at the WACC.
D) The horizon value must always be more than 20 years in the future.
E) The horizon value is calculated by discounting the free cash flows beyond the horizon date and any tax savings at the levered cost of equity.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One of the main reasons why foreign firms are interested in buying U.S.companies is to gain entrance to the U.S.market.A decline in the value of the dollar relative to most foreign currencies makes this competitive strategy especially attractive.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A company seeking to fight off a hostile takeover might employ the services of an investment banking firm to develop a defensive strategy.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Raymond Supply,a national hardware chain,is considering purchasing a smaller chain,Strauss & Glazer Parts (SGP) .Raymond's analysts project that the merger will result in the following incremental free cash flows,tax shields,and horizon values: 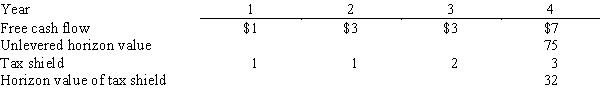 Assume that all cash flows occur at the end of the year.SGP is currently financed with 30% debt at a rate of 10%.The acquisition would be made immediately,and if it is undertaken,SGP would retain its current $15 million of debt and issue enough new debt to continue at the 30% target level.The interest rate would remain the same.SGP's pre-merger beta is 2.0,and its post-merger tax rate would be 34%.The risk-free rate is 8% and the market risk premium is 4%.What is the value of SGP to Raymond?
Assume that all cash flows occur at the end of the year.SGP is currently financed with 30% debt at a rate of 10%.The acquisition would be made immediately,and if it is undertaken,SGP would retain its current $15 million of debt and issue enough new debt to continue at the 30% target level.The interest rate would remain the same.SGP's pre-merger beta is 2.0,and its post-merger tax rate would be 34%.The risk-free rate is 8% and the market risk premium is 4%.What is the value of SGP to Raymond?
A) $53.40 million
B) $61.96 million
C) $64.64 million
D) $76.96 million
E) $79.64 million
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The distribution of synergistic gains between the stockholders of two merged firms is almost always based strictly on their respective market values before the announcement of the merger.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 49
Related Exams