A) If the WACC is 13%, Project A's NPV will be higher than Project B's.
B) If the WACC is 9%, Project A's NPV will be higher than Project B's.
C) If the WACC is 6%, Project B's NPV will be higher than Project A's.
D) If the WACC is greater than 14%, Project A's IRR will exceed Project B's.
E) If the WACC is 9%, Project B's NPV will be higher than Project A's.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) One defect of the IRR method versus the NPV is that the IRR does not take account of cash flows over a project's full life.
B) One defect of the IRR method versus the NPV is that the IRR does not take account of the time value of money.
C) One defect of the IRR method versus the NPV is that the IRR does not take account of the cost of capital.
D) One defect of the IRR method versus the NPV is that the IRR values a dollar received today the same as a dollar that will not be received until sometime in the future.
E) One defect of the IRR method versus the NPV is that the IRR does not take proper account of differences in the sizes of projects.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Jazz World Inc.is considering a project that has the following cash flow and WACC data.What is the project's NPV? Note that a project's projected NPV can be negative,in which case it will be rejected. 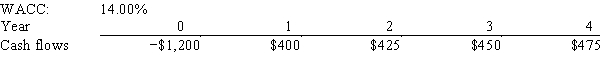
A) $41.25
B) $45.84
C) $50.93
D) $56.59
E) $62.88
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT? Assume that all projects being considered have normal cash flows and are equally risky.
A) If a project's IRR is equal to its WACC, then, under all reasonable conditions, the project's NPV must be negative.
B) If a project's IRR is equal to its WACC, then under all reasonable conditions, the project's IRR must be negative.
C) If a project's IRR is equal to its WACC, then under all reasonable conditions the project's NPV must be zero.
D) There is no necessary relationship between a project's IRR, its WACC, and its NPV.
E) When evaluating mutually exclusive projects, those projects with relatively long lives will tend to have relatively high NPVs when the cost of capital is relatively high.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The NPV method was once the favorite of academics and business executives, but today most authorities regard the MIRR as being the best indicator of a project's profitability.
B) If the cost of capital declines, this lowers a project's NPV.
C) The NPV method is regarded by most academics as being the best indicator of a project's profitability, hence most academics recommend that firms use only this one method and disregard other methods.
D) A project's NPV depends on the total amount of cash flows the project produces, but because the cash flows are discounted at the WACC, it does not matter if the cash flows occur early or late in the project's life.
E) The NPV and IRR methods may give different recommendations regarding which of two mutually exclusive projects should be accepted, but they always give the same recommendation regarding the acceptability of a normal, independent project.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If a project with normal cash flows has an IRR greater than the WACC, the project must also have a positive NPV.
B) If Project A's IRR exceeds Project B's, then A must have the higher NPV.
C) A project's MIRR can never exceed its IRR.
D) If a project with normal cash flows has an IRR less than the WACC, the project must have a positive NPV.
E) If the NPV is negative, the IRR must also be negative.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the economy is enjoying a strong boom,and as a result interest rates and money costs generally are relatively high.The WACC for two mutually exclusive projects that are being considered is 12%.Project S has an IRR of 20% while Project L's IRR is 15%.The projects have the same NPV at the 12% current WACC.However,you believe that the economy will soon fall into a mild recession,and money costs and thus your WACC will soon decline.You also think that the projects will not be funded until the WACC has decreased,and their cash flows will not be affected by the change in economic conditions.Under these conditions,which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) You should reject both projects because they will both have negative NPVs under the new conditions.
B) You should delay a decision until you have more information on the projects, even if this means that a competitor might come in and capture this market.
C) You should recommend Project L, because at the new WACC it will have the higher NPV.
D) You should recommend Project S, because at the new WACC it will have the higher NPV.
E) You should recommend Project L because it will have both a higher IRR and a higher NPV under the new conditions.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In theory,capital budgeting decisions should depend solely on forecasted cash flows and the opportunity cost of capital.The decision criterion should not be affected by managers' tastes,choice of accounting method,or the profitability of other independent projects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Projects S and L both have an initial cost of $10,000,followed by a series of positive cash inflows.Project S's undiscounted net cash flows total $20,000,while L's total undiscounted flows are $30,000.At a WACC of 10%,the two projects have identical NPVs.Which project's NPV is more sensitive to changes in the WACC?
A) Project S.
B) Project L.
C) Both projects are equally sensitive to changes in the WACC since their NPVs are equal at all costs of capital.
D) Neither project is sensitive to changes in the discount rate, since both have NPV profiles that are horizontal.
E) The solution cannot be determined because the problem gives us no information that can be used to determine the projects' relative IRRs.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When considering two mutually exclusive projects,the firm should always select the project whose internal rate of return is the highest,provided the projects have the same initial cost.This statement is true regardless of whether the projects can be repeated or not.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ehrmann Data Systems is considering a project that has the following cash flow and WACC data.What is the project's MIRR? Note that a project's projected MIRR can be less than the WACC (and even negative) ,in which case it will be rejected. 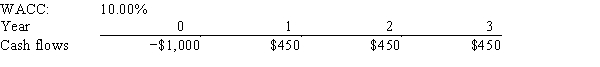
A) 9.32%
B) 10.35%
C) 11.50%
D) 12.78%
E) 14.20%
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When evaluating mutually exclusive projects,the modified IRR (MIRR)always leads to the same capital budgeting decisions as the NPV method,regardless of the relative lives or sizes of the projects being evaluated.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
McCall Manufacturing has a WACC of 10%.The firm is considering two normal,equally risky,mutually exclusive,but not repeatable projects.The two projects have the same investment costs,but Project A has an IRR of 15%,while Project B has an IRR of 20%.Assuming the projects' NPV profiles cross in the upper right quadrant,which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Each project must have a negative NPV.
B) Since the projects are mutually exclusive, the firm should always select Project B.
C) If the crossover rate is 8%, Project B will have the higher NPV.
D) Only one project has a positive NPV.
E) If the crossover rate is 8%, Project A will have the higher NPV.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The NPV method's assumption that cash inflows are reinvested at the cost of capital is generally more reasonable than the IRR's assumption that cash flows are reinvested at the IRR.This is an important reason why the NPV method is generally preferred over the IRR method.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Projects S and L both have normal cash flows,and the projects have the same risk,hence both are evaluated with the same WACC,10%.However,S has a higher IRR than L.Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Project S must have a higher NPV than Project L.
B) If Project S has a positive NPV, Project L must also have a positive NPV.
C) If the WACC falls, each project's IRR will increase.
D) If the WACC increases, each project's IRR will decrease.
E) If Projects S and L have the same NPV at the current WACC, 10%, then Project L, the one with the lower IRR, would have a higher NPV if the WACC used to evaluate the projects declined.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Resnick Inc.is considering a project that has the following cash flow data.What is the project's payback? 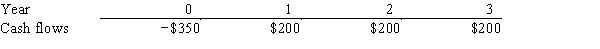
A) 1.42 years
B) 1.58 years
C) 1.75 years
D) 1.93 years
E) 2.12 years
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A conflict will exist between the NPV and IRR methods,when used to evaluate two equally risky but mutually exclusive projects,if the projects' cost of capital is less than the rate at which the projects' NPV profiles cross.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The NPV method is based on the assumption that projects' cash flows are reinvested at the project's risk-adjusted cost of capital.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Projects with "normal" cash flows can have only one real IRR.
B) Projects with "normal" cash flows can have two or more real IRRs.
C) Projects with "normal" cash flows must have two changes in the sign of the cash flows,
D) The "multiple IRR problem" can arise if a project's cash flows are "normal."
E) Projects with "nonnormal" cash flows are almost never encountered in the real world.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stern Associates is considering a project that has the following cash flow data.What is the project's payback? 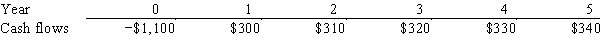
A) 2.31 years
B) 2.56 years
C) 2.85 years
D) 3.16 years
E) 3.52 years
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 108
Related Exams