B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Sunk costs must be considered if the IRR method is used but not if the firm relies on the NPV method.
B) A good example of a sunk cost is a situation where a bank opens a new office,and that new office leads to a decline in deposits of the bank's other offices.
C) A good example of a sunk cost is money that a banking corporation spent last year to investigate the site for a new office,then expensed that cost for tax purposes,and now is deciding whether to go forward with the project.
D) If sunk costs are considered and reflected in a project's cash flows,then the project's calculated NPV will be higher than it otherwise would be.
E) An example of a sunk cost is the cost associated with restoring the site of a strip mine once the ore has been depleted.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Puckett Inc.risk-adjusts its WACC to account for project risk.It uses a risk-adjusted project cost of capital of 8% for below-average risk projects,10% for average-risk projects,and 12% for above-average risk projects.Which of the following independent projects should Puckett accept,assuming that the company uses the NPV method when choosing projects?
A) Project B,which has below-average risk and an IRR = 8.5%.
B) Project C,which has above-average risk and an IRR = 11%.
C) Without information about the projects' NPVs we cannot determine which project(s) should be accepted.
D) All of these projects should be accepted.
E) Project A,which has average risk and an IRR = 9%.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Suppose Walker Publishing Company is considering bringing out a new finance text whose projected revenues include some revenues that will be taken away from another of Walker's books.The lost sales on the older book are a sunk cost and as such should not be considered in the analysis for the new book.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Superior analytical techniques,such as NPV,used in combination with risk-adjusted cost of capital estimates,can overcome the problem of poor cash flow estimation and lead to generally correct accept/reject decisions.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A firm that bases its capital budgeting decisions on either NPV or IRR will be more likely to accept a given project if it uses accelerated depreciation than if it uses straight-line depreciation,other things being equal.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In cash flow estimation,the existence of externalities should be taken into account if those externalities have any effects on the firm's long-run cash flows.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Any cash flows that can be classified as incremental to a particular project⎯i.e. ,results directly from the decision to undertake the project⎯should be reflected in the capital budgeting analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
We can identify the cash costs and cash inflows to a company that will result from a project.These could be called "direct inflows and outflows," and the net difference is the direct net cash flow.If there are other costs and benefits that do not flow from or to the firm,but to other parties,these are called externalities,and they need not be considered as a part of the capital budgeting analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Under current laws and regulations,corporations must use straight-line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 5 years or longer.
B) Corporations must use the same depreciation method (e.g. ,straight line or accelerated) for stockholder reporting and tax purposes.
C) Since depreciation is not a cash expense,it has no effect on cash flows and thus no effect on capital budgeting decisions.
D) Under accelerated depreciation,higher depreciation charges occur in the early years,and this reduces the early cash flows and thus lowers a project's projected NPV.
E) Using accelerated depreciation rather than straight line would normally have no effect on a project's total projected cash flows but it would affect the timing of the cash flows and thus the NPV.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Brandt Enterprises is considering a new project that has a cost of $1,000,000,and the CFO set up the following simple decision tree to show its three most likely scenarios.The firm could arrange with its work force and suppliers to cease operations at the end of Year 1 should it choose to do so,but to obtain this abandonment option,it would have to make a payment to those parties.How much is the option to abandon worth to the firm? 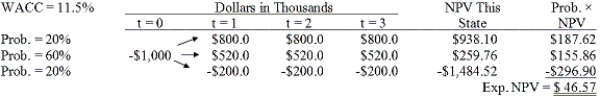
A) $55.08
B) $57.98
C) $61.03
D) $64.08
E) $67.29
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
McLeod Inc.is considering an investment that has an expected return of 15% and a standard deviation of 10%.What is the investment's coefficient of variation?
A) 0.67
B) 0.73
C) 0.81
D) 0.89
E) 0.98
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) An example of an externality is a situation where a bank opens a new office,and that new office causes deposits in the bank's other offices to decline.
B) The NPV method automatically deals correctly with externalities,even if the externalities are not specifically identified,but the IRR method does not.This is another reason to favor the NPV.
C) Both the NPV and IRR methods deal correctly with externalities,even if the externalities are not specifically identified.However,the payback method does not.
D) Identifying an externality can never lead to an increase in the calculated NPV.
E) An externality is a situation where a project would have an adverse effect on some other part of the firm's overall operations.If the project would have a favorable effect on other operations,then this is not an externality.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The use of accelerated versus straight-line depreciation causes net income reported to stockholders to be lower,and cash flows higher,during every year of a project's life,other things held constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Under current laws and regulations,corporations must use straight-line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 5 years or longer.
B) Corporations must use the same depreciation method for both stockholder reporting and tax purposes.
C) Using accelerated depreciation rather than straight line normally has the effect of speeding up cash flows and thus increasing a project's forecasted NPV.
D) Using accelerated depreciation rather than straight line normally has no effect on a project's total projected cash flows nor would it affect the timing of those cash flows or the resulting NPV of the project.
E) Since depreciation is a cash expense,the faster an asset is depreciated,the lower the projected NPV from investing in the asset.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Accelerated depreciation has an advantage for profitable firms in that it moves some cash flows forward,thus increasing their present value.On the other hand,using accelerated depreciation generally lowers the reported current year's profits because of the higher depreciation expenses.However,the reported profits problem can be solved by using different depreciation methods for tax and stockholder reporting purposes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is extremely difficult to estimate the revenues and costs associated with large,complex projects that take several years to develop.This is why subjective judgment is often used for such projects along with discounted cash flow analysis.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) One advantage of sensitivity analysis relative to scenario analysis is that it explicitly takes into account the probability of specific effects occurring,whereas scenario analysis cannot account for probabilities.
B) Well-diversified stockholders do not need to consider market risk when determining required rates of return.
C) Market risk is important,but it does not have a direct effect on stock prices because it only affects beta.
D) Simulation analysis is a computerized version of scenario analysis where input variables are selected randomly on the basis of their probability distributions.
E) Sensitivity analysis is a good way to measure market risk because it explicitly takes into account diversification effects.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Typically,a project will have a higher NPV if the firm uses accelerated rather than straight-line depreciation.This is because the total cash flows over the project's life will be higher if accelerated depreciation is used,other things held constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Under current laws and regulations,corporations must use straight-line depreciation for all assets whose lives are 3 years or longer.
B) If firms use accelerated depreciation,they will write off assets slower than they would under straight-line depreciation,and as a result projects' forecasted NPVs are normally lower than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes.
C) If they use accelerated depreciation,firms can write off assets faster than they could under straight-line depreciation,and as a result projects' forecasted NPVs are normally lower than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes.
D) If they use accelerated depreciation,firms can write off assets faster than they could under straight-line depreciation,and as a result projects' forecasted NPVs are normally higher than they would be if straight-line depreciation were required for tax purposes.
E) Since depreciation is not a cash expense,and since cash flows and not accounting income are the relevant input,depreciation plays no role in capital budgeting.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 61
Related Exams