B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your 75-year-old grandmother expects to live for another 15 years. She currently has $1,000,000 of savings, which is invested to earn a guaranteed 5% rate of return. If inflation averages 2% per year, how much can she withdraw (to the nearest dollar) at the beginning of each year and keep the withdrawals constant in real terms, i.e., growing at the same rate as inflation and thus enabling her to maintain a constant standard of living?
A) $65,632
B) $72,925
C) $81,027
D) $89,130
E) $98,043
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you deposited $5,000 in a bank account that pays 5.25% with daily compounding based on a 360-day year. How much would be in the account after 8 months, assuming each month has 30 days?
A) $5,178.09
B) $5,436.99
C) $5,708.84
D) $5,994.28
E) $6,294.00
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the present value of the following cash flow stream at a rate of 8.0%? 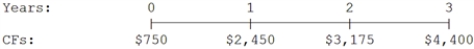
A) $7,917
B) $8,333
C) $8,772
D) $9,233
E) $9,695
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If some cash flows occur at the beginning of the periods while others occur at the ends, then we have what the textbook defines as a variable annuity.
B) The cash flows for an ordinary (or deferred) annuity all occur at the beginning of the periods.
C) If a series of unequal cash flows occurs at regular intervals, such as once a year, then the series is by definition an annuity.
D) The cash flows for an annuity due must all occur at the beginning of the periods.
E) The cash flows for an annuity may vary from period to period, but they must occur at regular intervals, such as once a year or once a month.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pacific Bank pays a 4.50% nominal rate on deposits, with monthly compounding. What effective annual rate (EFF%) does the bank pay?
A) 3.72%
B) 4.13%
C) 4.59%
D) 5.05%
E) 5.56%
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How much would Roderick have after 6 years if he has $500 now and leaves it invested at 5.5% with annual compounding?
A) $591.09
B) $622.20
C) $654.95
D) $689.42
E) $723.89
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A salt mine you inherited will pay you $25,000 per year for 25 years, with the first payment being made today. If you think a fair return on the mine is 7.5%, how much should you ask for it if you decide to sell it?
A) $284,595
B) $299,574
C) $314,553
D) $330,281
E) $346,795
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you are buying your first home for $145,000, and you have $15,000 for your down payment. You have arranged to finance the remainder with a 30-year, monthly payment, amortized mortgage at a 6.5% nominal interest rate, with the first payment due in one month. What will your monthly payments be?
A) $741.57
B) $780.60
C) $821.69
D) $862.77
E) $905.91
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) An investment that has a nominal rate of 6% with semiannual payments will have an effective rate that is smaller than 6%.
B) The present value of a 3-year, $150 annuity due will exceed the present value of a 3-year, $150 ordinary annuity.
C) If a loan has a nominal annual rate of 8%, then the effective rate can never be greater than 8%.
D) If a loan or investment has annual payments, then the effective, periodic, and nominal rates of interest will all be different.
E) The proportion of the payment that goes toward interest on a fully amortized loan increases over time.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your older brother turned 35 today, and he is planning to save $7,000 per year for retirement, with the first deposit to be made one year from today. He will invest in a mutual fund that's expected to provide a return of 7.5% per year. He plans to retire 30 years from today, when he turns 65, and he expects to live for 25 years after retirement, to age 90. Under these assumptions, how much can he spend each year after he retires? His first withdrawal will be made at the end of his first retirement year.
A) $58,601
B) $61,686
C) $64,932
D) $68,179
E) $71,588
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you earned a $275,000 bonus this year and invested it at 8.25% per year. How much could you withdraw at the end of each of the next 20 years?
A) $28,532
B) $29,959
C) $31,457
D) $33,030
E) $34,681
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What annual payment must you receive in order to earn a 6.5% rate of return on a perpetuity that has a cost of $1,250?
A) $77.19
B) $81.25
C) $85.31
D) $89.58
E) $94.06
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If CF0 is positive and all the other CFs are negative, then you can still solve for I.
B) If you have a series of cash flows, each of which is positive, you can solve for I, where the solution value of I causes the PV of the cash flows to equal the cash flow at Time 0.
C) If you have a series of cash flows, and CF0 is negative but each of the following CFs is positive, you can solve for I, but only if the sum of the undiscounted cash flows exceeds the cost.
D) To solve for I, one must identify the value of I that causes the PV of the positive CFs to equal the absolute value of the FV of the negative CFs. It is impossible to find the value of I without a computer or financial calculator.
E) If you solve for I and get a negative number, then you must have made a mistake.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose People's bank offers to lend you $10,000 for 1 year on a loan contract that calls for you to make interest payments of $250.00 at the end of each quarter and then pay off the principal amount at the end of the year. What is the effective annual rate on the loan?
A) 8.46%
B) 8.90%
C) 9.37%
D) 9.86%
E) 10.38%
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the present value of the following cash flow stream at a rate of 12.0%? 
A) $9,699
B) $10,210
C) $10,747
D) $11,284
E) $11,849
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How much would $100, growing at 5% per year, be worth after 75 years?
A) $3,689.11
B) $3,883.27
C) $4,077.43
D) $4,281.30
E) $4,495.37
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose a State of New Mexico bond will pay $1,000 eight years from now. If the going interest rate on these 8-year bonds is 5.5%, how much is the bond worth today?
A) $651.60
B) $684.18
C) $718.39
D) $754.31
E) $792.02
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Your aunt has $500,000 invested at 5.5%, and she now wants to retire. She wants to withdraw $45,000 at the beginning of each year, beginning immediately. When she makes her last withdrawal (at the beginning of a year) , she also wants to have enough left in the account so that you can make a final withdrawal of $50,000 at the end of that year (her last withdrawal is at the beginning of the year, your withdrawal is at the end of that same year) . What is the maximum number of $45,000 withdrawals that she can make and still have enough in the account so that you can make a $50,000 withdrawal at the end of the year of her last withdrawal? (Hint: If your solution for N is not an integer, round down to the nearest whole number.)
A) 13
B) 14
C) 15
D) 16
E) 17
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are offered a chance to buy an asset for $7,250 that is expected to produce cash flows of $750 at the end of Year 1, $1,000 at the end of Year 2, $850 at the end of Year 3, and $6,250 at the end of Year 4. What rate of return would you earn if you bought this asset?
A) 4.93%
B) 5.19%
C) 5.46%
D) 5.75%
E) 6.05%
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 168
Related Exams