A) To find the MIRR, we first compound cash flows at the regular IRR to find the TV, and then we discount the TV at the cost of capital to find the PV.
B) The NPV and IRR methods both assume that cash flows can be reinvested at the cost of capital. However, the MIRR method assumes reinvestment at the MIRR itself.
C) If two projects have the same cost, and if their NPV profiles cross in the upper right quadrant, then the project with the higher IRR probably has more of its cash flows coming in the later years.
D) If two projects have the same cost, and if their NPV profiles cross in the upper right quadrant, then the project with the lower IRR probably has more of its cash flows coming in the later years.
E) For a project with normal cash flows, any change in the cost of capital will change both the NPV and the IRR.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) The discounted payback method recognizes all cash flows over a project's life, and it also adjusts these cash flows to account for the time value of money.
B) The regular payback method was, years ago, widely used, but virtually no companies even calculate the payback today.
C) The regular payback is useful as an indicator of a project's liquidity because it gives managers an idea of how long it will take to recover the funds invested in a project.
D) The regular payback does not consider cash flows beyond the payback year, but the discounted payback overcomes this defect.
E) The regular payback method recognizes all cash flows over a project's life.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If you were evaluating two mutually exclusive projects for a firm with a zero cost of capital, the payback method and NPV method would always lead to the same decision on which project to undertake.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carolina Company is considering Projects S and L, whose cash flows are shown below. These projects are mutually exclusive, equally risky, and are not repeatable. If the decision is made by choosing the project with the higher IRR, how much value will be forgone? Note that under some conditions choosing projects on the basis of the IRR will cause $0.00 value to be lost. 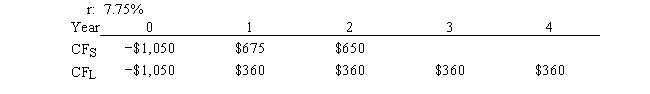
A) $11.45
B) $12.72
C) $14.63
D) $16.82
E) $19.35
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Conflicts between two mutually exclusive projects occasionally occur, where the NPV method ranks one project higher but the IRR method ranks the other one first. In theory, such conflicts should be resolved in favor of the project with the higher positive NPV.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Yoga Center Inc. is considering a project that has the following cash flow and cost of capital (r) data. What is the project's NPV? Note that a project's expected NPV can be negative, in which case it will be rejected. 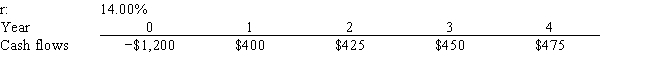
A) $41.25
B) $45.84
C) $50.93
D) $56.59
E) $62.88
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A project's IRR is independent of the firm's cost of capital. In other words, a project's IRR doesn't change with a change in the firm's cost of capital.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Corner Jewelers, Inc. recently analyzed the project whose cash flows are shown below. However, before the company decided to accept or reject the project, the Federal Reserve changed interest rates and therefore the firm's cost of capital (r) . The Fed's action did not affect the forecasted cash flows. By how much did the change in the r affect the project's forecasted NPV? Note that a project's expected NPV can be negative, in which case it should be rejected. 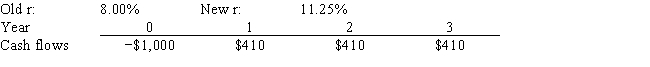
A) −$59.03
B) −$56.08
C) −$53.27
D) −$50.61
E) −$48.08
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Modern Refurbishing Inc. is considering a project that has the following cash flow data. What is the project's IRR? Note that a project's IRR can be less than the cost of capital (and even negative) , in which case it will be rejected. 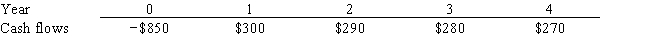
A) 13.13%
B) 14.44%
C) 15.89%
D) 17.48%
E) 19.22%
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pet World is considering a project that has the following cash flow data. What is the project's IRR? Note that a project's IRR can be less than the cost of capital (and even negative) , in which case it will be rejected. 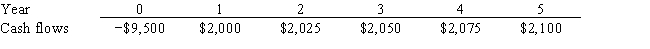
A) 2.08%
B) 2.31%
C) 2.57%
D) 2.82%
E) 3.10%
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Poder Inc. is considering a project that has the following cash flow data. What is the project's payback? 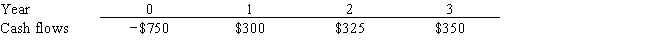
A) 1.91 years
B) 2.12 years
C) 2.36 years
D) 2.59 years
E) 2.85 years
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Current Design Co. is considering two mutually exclusive, equally risky, and not repeatable projects, S and L. Their cash flows are shown below. The CEO believes the IRR is the best selection criterion, while the CFO advocates the NPV. If the decision is made by choosing the project with the higher IRR rather than the one with the higher NPV, how much, if any, value will be forgone, i.e., what's the chosen NPV versus the maximum possible NPV? Note that (1) "true value" is measured by NPV, and (2) under some conditions the choice of IRR vs. NPV will have no effect on the value gained or lost. 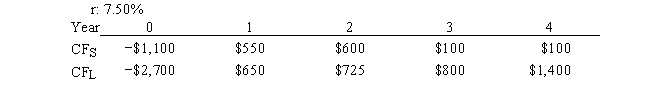
A) $138.10
B) $149.21
C) $160.31
D) $171.42
E) $182.52
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a project has normal cash flows. All else equal, which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) A project's NPV increases as the cost of capital declines.
B) A project's MIRR is unaffected by changes in the cost of capital.
C) A project's regular payback increases as the cost of capital declines.
D) A project's discounted payback increases as the cost of capital declines.
E) A project's IRR increases as the cost of capital declines.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Craig's Car Wash Inc. is considering a project that has the following cash flow and cost of capital (r) data. What is the project's discounted payback? 
A) 1.88 years
B) 2.09 years
C) 2.29 years
D) 2.52 years
E) 2.78 years
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The cost of capital for two mutually exclusive projects that are being considered is 8%. Project K has an IRR of 20% while Project R's IRR is 15%. The projects have the same NPV at the 8% current cost of capital. However, you believe that money costs and thus your cost of capital will also increase. You also think that the projects will not be funded until the cost of capital has increased, and their cash flows will not be affected by the change in economic conditions. Under these conditions, which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) You should delay a decision until you have more information on the projects, even if this means that a competitor might come in and capture this market.
B) You should recommend Project R, because at the new cost of capital it will have the higher NPV.
C) You should recommend Project K, because at the new cost of capital it will have the higher NPV.
D) You should recommend Project K because it has the higher IRR and will continue to have the higher IRR even at the new cost of capital.
E) You should reject both projects because they will both have negative NPVs under the new conditions.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Watts Co. is considering a project that has the following cash flow and cost of capital (r) data. What is the project's MIRR? Note that a project's MIRR can be less than the cost of capital (and even negative) , in which case it will be rejected. 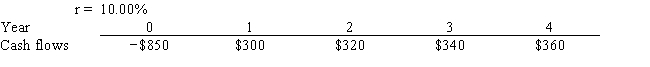
A) 14.08%
B) 15.65%
C) 17.21%
D) 18.94%
E) 20.83%
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Projects S and L are equally risky, mutually exclusive, and have normal cash flows. Project S has an IRR of 15%, while Project L's IRR is 12%. The two projects have the same NPV when the cost of capital is 7%. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) If the cost of capital is 6%, Project S will have the higher NPV.
B) If the cost of capital is 13%, Project S will have the lower NPV.
C) If the cost of capital is 10%, both projects will have a negative NPV.
D) Project S's NPV is more sensitive to changes in cost of capital than Project L's.
E) If the cost of capital is 10%, both projects will have positive NPVs.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT? Assume that the project being considered has normal cash flows, with one outflow followed by a series of inflows.
A) The lower the cost of capital used to calculate a project's NPV, the lower the calculated NPV will be.
B) If a project's NPV is less than zero, then its IRR must be less than the cost of capital.
C) If a project's NPV is greater than zero, then its IRR must be less than zero.
D) The NPV of a relatively low-risk project should be found using a relatively high cost of capital.
E) A project's NPV is found by compounding the cash inflows at the IRR to find the terminal value (TV) , then discounting the TV at the cost of capital.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Project S has a pattern of high cash flows in its early life, while Project L has a longer life, with large cash flows late in its life. Neither has negative cash flows after Year 0, and at the current cost of capital, the two projects have identical NPVs. Now suppose interest rates and money costs decline. Other things held constant, this change will cause L to become preferred to S.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Robbins Inc. is considering a project that has the following cash flow and cost of capital (r) data. What is the project's NPV? Note that if a project's expected NPV is negative, it should be rejected. 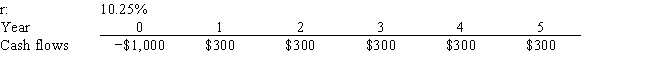
A) $105.89
B) $111.47
C) $117.33
D) $123.51
E) $130.01
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 108
Related Exams