A) Raise both taxes and expenditures by $40 billion dollars.
B) Raise both taxes and expenditures by $40 billion dollars
C) Reduce both taxes and expenditures by $10 billion dollars.
D) Reduce both taxes and expenditures by $10 billion dollars
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If expected inflation is constant, then when the nominal interest rate increases, the real interest rate
A) increases by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
B) increases by the change in the nominal interest rate.
C) decreases by the change in the nominal interest rate.
D) decreases by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following events would shift money demand to the left?
A) an increase in the price level
B) a decrease in the price level
C) an increase in the interest rate
D) a decrease in the interest rate
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory, a decrease in the price level shifts the
A) money demand curve rightward, so the interest rate increases.
B) money demand curve rightward, so the interest rate decreases.
C) money demand curve leftward, so the interest rate decreases.
D) money demand curve leftward, so the interest rate increases.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed increases the money supply,
A) the interest rate increases, which tends to raise stock prices.
B) the interest rate increases, which tends to reduce stock prices.
C) the interest rate decreases, which tends to raise stock prices.
D) the interest rate decreases, which tends to reduce stock prices.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the interest rate falls,
A) the quantity of money demanded falls, which would reduce a shortage.
B) the quantity of money demanded falls, which would reduce a surplus.
C) the quantity of money demanded rises, which would reduce a shortage.
D) the quantity of money demanded rises, which would reduce a surplus.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-2. On the left-hand graph, MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph, AD represents aggregate demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs.
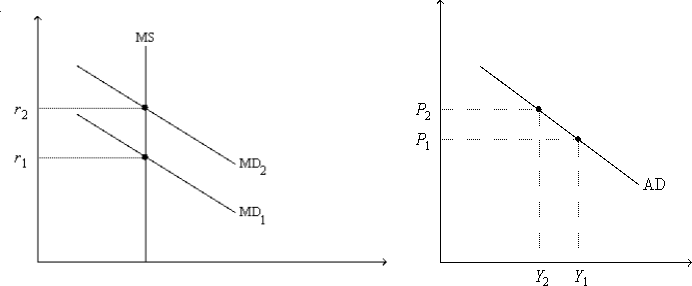 -Refer to Figure 16-2. As we move from one point to another along the money-demand curve MD1,
-Refer to Figure 16-2. As we move from one point to another along the money-demand curve MD1,
A) the price level is held fixed at P1.
B) the interest rate is held fixed at r1.
C) the money supply is changing so as to keep the money market in equilibrium.
D) the expected inflation rate is changing so as to keep the real interest rate constant.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the inflation rate is zero, then
A) both the nominal interest rate and the real interest rate can fall below zero.
B) the nominal interest rate can fall below zero, but the real interest rate cannot fall below zero.
C) the real interest rate can fall below zero, but the nominal interest rate cannot fall below zero.
D) neither the nominal interest rate nor the real interest rate can fall below zero.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following raises the interest rate?
A) an increase in government expenditures and an increase in the money supply
B) an increase in government expenditures and a decrease in the money supply
C) a decrease in government expenditures and an increase in the money supply
D) a decrease in government expenditures and a decrease in the money supply
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following policies would Keynes's followers support when an increase in business optimism shifts the aggregate demand curve away from long-run equilibrium?
A) decrease taxes
B) increase government expenditures
C) increase the money supply
D) None of the above is correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is excess money supply, people will
A) deposit more into interest-bearing accounts, and the interest rate will fall.
B) deposit more into interest-bearing accounts, and the interest rate will rise.
C) withdraw money from interest-bearing accounts, and the interest rate will fall.
D) withdraw money from interest-bearing accounts, and the interest rate will rise.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During recessions, automatic stabilizers tend to make the government's budget
A) move toward deficit.
B) move toward surplus.
C) move toward balance.
D) not necessarily move the budget in any particular direction.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The lag problem associated with fiscal policy is due mostly to
A) the fact that business firms make investment plans far in advance.
B) the political system of checks and balances that slows down the process of implementing fiscal policy.
C) the time it takes for changes in government spending or taxes to affect the interest rate.
D) All of the above are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When the Fed announces a target for the federal funds rate, it essentially accommodates the day-to-day fluctuations in money demand by adjusting the money supply accordingly.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynes used the term "animal spirits" to refer to
A) policy makers harming the economy in the pursuit of self interest.
B) arbitrary changes in attitudes of household and firms.
C) mean-spirited economists who believed in the classical dichotomy.
D) firms' relentless efforts to maximize profits.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If expected inflation is constant, then when the nominal interest rate falls, the real interest rate
A) falls by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
B) falls by the change in the nominal interest rate.
C) rises by the change in the nominal interest rate.
D) rises by more than the change in the nominal interest rate.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Stock prices often rise when the Fed raises interest rates.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the multiplier is 6.25, then the MPC is
A) 0.2.
B) 0.6.
C) 0.75.
D) 0.84.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the interest rate is above the Fed's target, the Fed should
A) buy bonds to increase the money supply.
B) buy bonds to decrease the money supply.
C) sell bonds to increase the money supply.
D) sell bonds to decrease the money supply.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Keynes argued that aggregate demand is
A) stable, because the economy tends to return to its long-run equilibrium quickly after any disturbance to aggregate demand.
B) stable, because changes in consumption are mostly offset by changes in investment and vice versa.
C) unstable, because waves of pessimism and optimism create fluctuations in aggregate demand.
D) unstable, because of long and variable policy lags that worsen economic fluctuations.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 416
Related Exams