A) a hidden action.
B) a hidden characteristic.
C) adverse selection.
D) the Condorcet Paradox.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-15
Diane, Henry, and Linda are voting for who to promote. They can only promote one candidate. Their preferences are given in the table below. 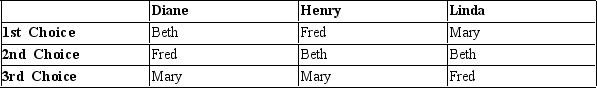 -Refer to Table 22-15. If the vote were conducted according to a Borda count system where each person's first choice receives 3 points, second choice 2 points, and third choice 1 point,
-Refer to Table 22-15. If the vote were conducted according to a Borda count system where each person's first choice receives 3 points, second choice 2 points, and third choice 1 point,
A) Beth would win.
B) Fred would win.
C) Mary would win.
D) Fred and Mary would tie.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a characteristic of a corporation but not of a small family-owned business?
A) The corporation buys inputs in markets for the factors of production.
B) The corporation sells output in markets for goods and services.
C) The corporation is guided in its decisions by the objective of profit maximization.
D) The corporation faces a principal-agent problem created by the separation of ownership and control.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person who makes decisions that are "merely good enough" is called a(n)
A) optimizer.
B) rational person.
C) satisficer.
D) maxi-minimizer.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One of the things that employers can do to lessen the moral hazard problem involving their employees is to pay them in advance for their work.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-12
The following table shows the preferences for the five voters in a city regarding how to deal with the city's diseased trees. 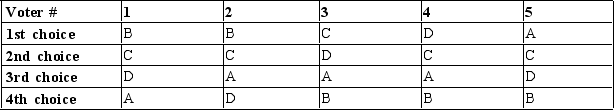 A = do nothing
B = follow the expert's advice to remove every tree
C = remove every 4th tree now and perhaps more later D = use an untested spraying alternative
-Refer to Table 22-12. Consider the public policy for dealing with diseased trees. Based on the preferences in the table, which of the following statements is correct?
A = do nothing
B = follow the expert's advice to remove every tree
C = remove every 4th tree now and perhaps more later D = use an untested spraying alternative
-Refer to Table 22-12. Consider the public policy for dealing with diseased trees. Based on the preferences in the table, which of the following statements is correct?
A) Outcome D is preferred to outcome C overall.
B) Outcome B is preferred to outcome C overall.
C) Outcome D is preferred to outcome B overall.
D) Outcome A is preferred to outcome D overall.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Conventional economic theory assumes that people
A) care a great deal about fairness.
B) are inconsistent over time in their decisionmaking.
C) are rational.
D) are satisficers.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-16
The Johnson family is planning a vacation and, though Mr. and Mrs. Johnson will be paying for the trip, they have decided to use a democratic voting process to choose their destination. The family members' preferences are reflected in the table below. 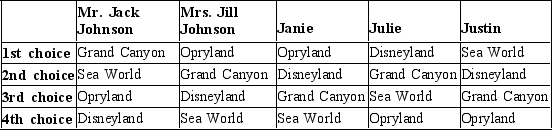 -Refer to Table 22-16. Mr. Johnson recommends using a vote by majority rule. If he wants to ensure that his 1st choice becomes the family's winning destination, he should propose
-Refer to Table 22-16. Mr. Johnson recommends using a vote by majority rule. If he wants to ensure that his 1st choice becomes the family's winning destination, he should propose
A) first choosing between Opryland and the Grand Canyon, then choosing between the winner of the first vote and Sea World, and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and Disneyland.
B) first choosing between Disneyland and Sea World, then choosing between the winner of the first vote and the Grand Canyon and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and the Opryland.
C) first choosing between Sea World and the Grand Canyon, then choosing between the winner of the first vote and Disneyland, and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and Opryland.
D) first choosing between Opryland and Disneyland, then choosing between the winner of the first vote and the Grand Canyon, and finally choosing between the winner of the second vote and Sea World.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Principles of Microeconomics professor wants to know how much prior knowledge her students have before beginning the class so she gives them a pre-test. This action is an example of
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) adverse selection.
D) moral hazard.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm with a very good product
A) has a higher cost of signaling (advertising) than does a firm with an inferior product.
B) has more to gain by signaling (advertising) than does a firm with an inferior product.
C) does not need to signal (advertise) because the product's quality speaks for itself.
D) will signal (advertise) effectively if signaling is free.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
When asked to give a range for the height of the tallest mountain in North America such that people were 90 percent confident the true number falls within it, most people gave ranges that were
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When new professors are hired, their job performance is monitored closely. If they meet their institution's standards, they will eventually receive tenure. After receiving tenure, professors' job performance is less closely monitored, and they become difficult to fire. Tenure thus creates
A) adverse selection.
B) a Condorcet paradox.
C) a screening problem.
D) a moral hazard problem.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mankiw argues that a primary difference between taxing products like gasoline and taxing soda and other sugary drinks is that
A) consumption of gasoline causes negative externalities on society while consumption of soda affects the consumer.
B) the government can generate significant revenue from the gas tax but not from a soda tax.
C) gasoline has inelastic demand but soda has elastic demand.
D) Both a and c are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An example of screening is a company spending a large sum on advertising to convey the high quality of its product.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A life insurance company requires new applicants to have a medical exam prior to writing the insurance policy. This requirement is an example of
A) signaling.
B) screening.
C) moral hazard.
D) adverse selection.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-4
The fortunate residents of Anytown have a budget surplus. The mayor decided that it is only fair to have the residents vote on what to do with the surplus. The mayor has narrowed the options down to three possible projects: a playground, a library, or a swimming pool. The voters fall into three categories and have preferences as illustrated in the table. 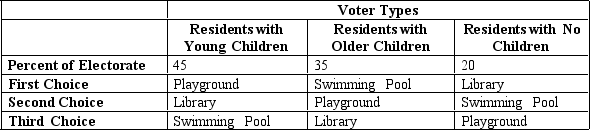 -Refer to Table 22-4. If the mayor decides to use a Borda count rather than pairwise voting,
-Refer to Table 22-4. If the mayor decides to use a Borda count rather than pairwise voting,
A) the swimming pool will win.
B) the library will win.
C) the playground will win.
D) the results will be the same as with pairwise voting.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Riley travels a great deal, and over the past several years he has read dozens of reviews of hotel chains, all of which rave about the clean rooms and great service at Comeon Inns. Last month, Riley checked into a room at a Comeon Inn for the first time, only to find the room filthy and the service lousy. He decided the Comeon Inn chain is inferior to other hotel chains.
A) Riley was irrational to have believed the reviews that he had read.
B) Riley was rational to have changed his mind about Comeon Inns based on his one experience.
C) Riley is an example of someone who gives too much weight to a small number of vivid observations.
D) Riley is an example of someone who is reluctant to change his mind.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-17
Voter Type 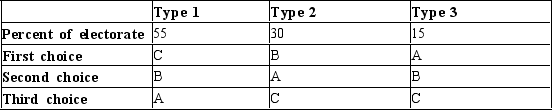 -Refer to Table 22-17. The table shows the preferences of three types of voters over three possible outcomes: A, B, and C. The table also shows the percentage of voters of each type. Based on this information, which voter type is the median voter?
-Refer to Table 22-17. The table shows the preferences of three types of voters over three possible outcomes: A, B, and C. The table also shows the percentage of voters of each type. Based on this information, which voter type is the median voter?
A) Type 1
B) Type 2
C) Type 3
D) The median voter cannot be determined without knowing the pair of outcomes from which the voters will be choosing.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 22-18
The following table shows the preferences of four types of voters over four possible alternatives as well as the percentage of the electorate with the given preferences. 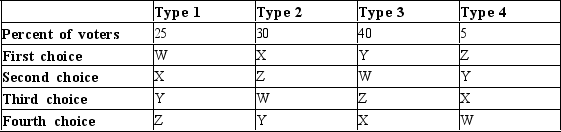 -Refer to Table 22-18. In a majority vote between alternatives X and Y, what percentage of the votes would X receive?
-Refer to Table 22-18. In a majority vote between alternatives X and Y, what percentage of the votes would X receive?
A) 35%
B) 45%
C) 55%
D) 65%
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A travel agency offers a money-back guarantee for vacationers taking their first cruise in case they do not enjoy the experience. This guarantee is an example of
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 341 - 360 of 440
Related Exams