B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Data on Shick Inc.for last year are shown below,along with the days sales outstanding of the firms against which it benchmarks.The firm's new CFO believes that the company could reduce its receivables enough to reduce its DSO to the benchmarks' average.If this were done,by how much would receivables decline? Use a 365-day year. 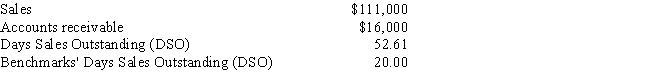
A) $9,124
B) $8,331
C) $12,100
D) $9,918
E) $7,538
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) A firm that makes 90% of its sales on credit and 10% for cash is growing at a constant rate of 10% annually.Such a firm will be able to keep its accounts receivable at the current level,since the 10% cash sales can be used to finance the 10% growth rate.
B) In managing a firm's accounts receivable,it is possible to increase credit sales per day yet still keep accounts receivable fairly steady,provided the firm can shorten the length of its collection period (its DSO) sufficiently.
C) Because of the costs of granting credit,it is not possible for credit sales to be more profitable than cash sales.
D) Since receivables and payables both result from sales transactions,a firm with a high receivables-to-sales ratio must also have a high payables-to-sales ratio.
E) Other things held constant,if a firm can shorten its DSO,this will lead to a higher current ratio.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Depreciation is included in the estimate of free cash flows (FCF = EBIT(1 - T) + Depreciation - [Capital expenditures + ΔNOWC]) ,hence depreciation is set forth on a separate line in the cash budget.
B) If cash inflows from collections occur in equal daily amounts but most payments must be made on the 10th of each month,then a regular monthly cash budget will be misleading.The problem can be corrected by using a daily cash budget.
C) Sound working capital policy is designed to maximize the time between cash expenditures on materials and the collection of cash on sales.
D) If a firm wants to generate more cash flow from operations in the next month or two,it could change its credit policy from 2/10,net 30 to net 60.
E) If a firm sells on terms of net 90,and if its sales are highly seasonal,with 80% of its sales in September,then its DSO as it is typically calculated (with sales per day = Sales for past 12 months/365) would probably be lower in October than in August.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Atlanta Cement,Inc.buys on terms of 2/15,net 30.It does not take discounts,and it typically pays 65 days after the invoice date.Net purchases amount to $720,000 per year.What is the nominal annual percentage cost of its non-free trade credit,based on a 365-day year?
A) 16.83%
B) 14.90%
C) 11.17%
D) 12.51%
E) 14.60%
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
One of the effects of ceasing to take trade credit discounts is that the firm's accounts payable will rise,other things held constant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Since receivables and payables both result from sales transactions,a firm with a high receivables-to-sales ratio must also have a high payables-to-sales ratio.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The concept of permanent current assets reflects the fact that some components of current assets do not shrink to zero even when a business is at its seasonal or cyclical low.Thus,permanent current assets represent a minimum level of current assets that must be financed.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A revolving credit agreement is a formal line of credit.The firm must generally pay a fee on the unused balance of the committed funds to compensate the bank for the commitment to extend those funds.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dewey Corporation has the following data,in thousands.Assuming a 365-day year,what is the firm's cash conversion cycle? Round your answer to the nearest day. 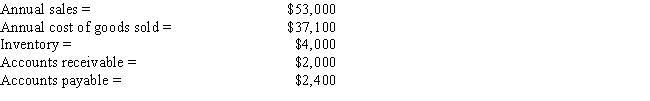
A) 29 days
B) 25 days
C) 30 days
D) 36 days
E) 33 days
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a profitable firm finds that it simply must "stretch" its accounts payable,then this suggests that it is undercapitalized,i.e. ,that it needs more working capital to support its operations.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dyl Pickle Inc.had credit sales of $4,000,000 last year and its days sales outstanding was DSO = 35 days.What was its average receivables balance,based on a 365-day year.
A) $441,096
B) $471,781
C) $368,219
D) $318,356
E) $383,562
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Shorter-term cash budgets (such as a daily cash budget for the next month)are generally used for actual cash control while longer-term cash budgets (such as a monthly cash budgets for the next year)are generally used for planning purposes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Madura Inc.wants to increase its free cash flow by $180 million during the coming year,which should result in a higher EVA and stock price.The CFO has made these projections for the upcoming year: 
What increase in net operating working capital (in millions of dollars) would enable the firm to meet its target increase in FCF?
What increase in net operating working capital (in millions of dollars) would enable the firm to meet its target increase in FCF?
A) $176
B) $156
C) $117
D) $161
E) $137
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aggarwal Inc.buys on terms of 2/10,net 30,and it always pays on the 30th day.The CFO calculates that the average amount of costly trade credit carried is $350,000.What is the firm's average accounts payable balance? Assume a 365-day year.
A) $425,250
B) $504,000
C) $525,000
D) $556,500
E) $514,500
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT commonly regarded as being a credit policy variable?
A) Credit period.
B) Collection policy.
C) Credit standards.
D) Cash discounts.
E) Payments deferral period.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The cash conversion cycle (CCC)combines three factors: The inventory conversion period,the receivables collection period,and the payables deferral period,and its purpose is to show how long a firm must finance its working capital.Other things held constant,the shorter the CCC,the more effective the firm's working capital management.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The calculated cost of trade credit for a firm that buys on terms of 2/10,net 30,is lower (other things held constant)if the firm plans to pay in 40 days than in 30 days.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Changes in a firm's collection policy can affect sales,working capital,and profits.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A) Net working capital is defined as current assets minus the difference between current liabilities and notes payable,and any increase in the current ratio automatically indicates that net working capital has increased.
B) Although short-term interest rates have historically averaged less than long-term rates,the heavy use of short-term debt is considered to be an aggressive strategy because of the inherent risks associated with using short-term financing.
C) If a company follows a policy of "matching maturities",this means that it matches its use of common stock with its use of long-term debt as opposed to short-term debt.
D) Net working capital is defined as current assets minus the difference between current liabilities and notes payable,and any decrease in the current ratio automatically indicates that net working capital has decreased.
E) If a company follows a policy of "matching maturities",this means that it matches its use of short-term debt with its use of long-term debt.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 124
Related Exams